Category: Medical
Every now and then we people complain about our lives, our status and our Health and so on so that we have a never-ending lists of complains. Such a situation or even every situation should be analysed according to Quran and Sunnah that why we are being created, should we complain to Allah or consider life as a test or what. The main purpose to write this post is to refresh and realise the purpose of our creation and act according to what Allah has told us in Quran.
So, lets have a glance below to learn what life actually is!!
First of All our purpose of creation as mentioned by The Holy Quran as follows,
[Quran Surah Adh Dhariyat 51:56] I have only created Jinns and men, that they may serve Me.
So the purpose of creation is very well told in this verse of Holy Quran.
[Quran Surah Al-Mulk 67:2] He Who created Death and Life, that He may try which of you is best in deed: and He is the Exalted in Might, Oft-Forgiving;-
So, its quite clear from the Ayah above that life is a test. which is mentioned in many of the Ayahs below,
[Quran Surah Al-Baqarah 2:155] Be sure we shall test you with something of fear and hunger, some loss in goods or lives or the fruits (of your toil), but give glad tidings to those who patiently persevere,
[Quran Surah Al-Baqarah 2:156] Who say, when afflicted with calamity: “To Allah (God) We belong, and to Him is our return”:-
[Quran Surah Al-Baqarah 2:157] They are those on whom (Descend) blessings from Allah (God), and Mercy, and they are the ones that receive guidance.
Allah test His creations in many ways and only those will be successful who are steadfast and believe on Allah alone. Allah test His believers by atrocities and affilictions and we should not assume them as the punishment from Allah and signs that Allah is displeased with us or doesn’t like us etc etc. Likewise, we should never construe the success and pleasures that others enjoy as signs that Allah is pleased with them or that they are privileged. Allah has given us the will to do good or bad and this is the way Allah test us that we opt to do good or bad.
Allah expressed in the following ayat that everything in our lives – the good and the bad of it– is a trial for us. How will we cope in the situation that Allah has placed for us? Will we be grateful in prosperity and patient in affliction or will we be arrogant and disobedient?
[Quran Surah Al-Anbiya 21:35] Every soul shall have a taste of death: and We test you by evil and by good by way of trial. to Us must ye return.
[Quran Surah Al-Fajr 89:15] Now, as for man, when his Lord trieth him, giving him honour and gifts, then saith he, (puffed up), “My Lord hath honoured me.”
[Quran Surah Al-Fajr 89:16] But when He trieth him, restricting his subsistence for him, then saith he (in despair), “My Lord hath humiliated me!”
[Quran Surah Al-Anbiya 21:23] He cannot be questioned for His acts, but they will be questioned (for theirs).
As expressed in Ayat below,
[Quran Surah Al-Nahl 16:9] And unto Allah (God) leads straight the Way, but there are ways that turn aside: if Allah (God) had willed, He could have guided all of you.
Allah has power over all universe, He can make everyone pious and good but then it will not be a test and justice. Justice is that one will be given free will to opt between good and bad and then what that person decides he is destined to get reward or punishment. Like suppose we know that Allah will give us “rizq” but the source of that, we have to choose- whether we are going to have Halal or get it Haram way. One should realise that Allah doesnt need us rather we need His help, blessings and mercy.
[Quran Surah Fatir 35:15] O ye men! It is ye that have need of Allah (God): but Allah (God) is the One Free of all wants, worthy of all praise.
We can never doubt on the power of Allah as He has the power over all universe and He can do want He want to. We can’t blame Him as He loves us seventy times more than ur mother do!!
|
Muscles of Gluteal Region
|
||||
|
Muscle
|
Origin
|
Insertion
|
Nerve
|
Action
|
|
gluteus maximus
|
outer surface of ilium, sacrum, coccyx, sacrotuberous ligament
|
iliotibial tract and gluteal tuberosity of femur
|
inferior gluteal nerve
|
extends & laterally rotates thigh; through iliotibial tract, it extends knee joint
|
|
gluteus medius
|
outer surface of ilium
|
greater trochanter of femur
|
superior gluteal nerve
|
abducts thigh. Tilts pelvis when walking
|
|
gluteus minimus
|
outer surface of ilium
|
greater trochanter of femur
|
superior gluteal nerve
|
abduct thigh; anterior fibers medially rotate thigh
|
|
tensor fasciae latae
|
iliac crest
|
iliotibial tract
|
superior gluteal nerve
|
assists gluteus major in locking the knee into full extension
|
|
piriformis
|
anterior surface of sacrum
|
greater trochanteric fossa
|
1st & 2nd sacral nerves
|
lateral rotator of thigh
|
|
superior gemellus
|
spine of ischium
|
greater trochanteric fossa
|
sacral plexus
|
lateral rotator of thigh
|
|
obturator internus
|
inner surface of obturator membrane
|
greater trochanteric fossa
|
sacral plexus
|
lateral rotator of thigh
|
|
inferior gemellus
|
ischial tuberosity
|
greater trochanteric fossa
|
sacral plexus
|
lateral rotator of thigh
|
|
obturator externus
|
outer surface of obturator membrane
|
greater trochanteric fossa of femur
|
obturator nerve
|
lateral rotator of thigh
|
|
Anterior Compartment of Thigh
|
||||
|
sartorius
|
anterior superior iliac spine
|
upper medial surface of tibia
|
femoral nerve
|
flexes, abducts, laterally rotates thigh; flexes & medially rotates leg
|
|
iliacus
|
iliac fossa
|
with psoas into the lesser trochanter of femur
|
femoral nerve
|
flexes thigh on trunk; if thigh is fixed, it flexes the trunk onto the thigh as in sitting up
|
|
psoas
|
12th thoracic body; transverse process, bodies & intervertebral discs of the 5 lumbar vertebrae
|
lesser trochanter of femur along with iliacus
|
lumbar plexus
|
flexes thigh on trunk; if thigh fixed, it flexes trunk onto thigh as in sitting up
|
|
pectineus
|
superior ramus of pubis
|
upper end shaft of femur
|
femoral nerve
|
flexes and adducts thigh
|
|
quadriceps femoris, rectus femoris
|
straight head from anterior inferior iliac spine; reflected head from ilium above acetabulum
|
quadriceps tendon into patella; into tibial tuberosity by patellar tendon
|
femoral nerve
|
extension of leg
|
|
quadriceps femoris, vastus lateralis
|
upper end and shaft of femur
|
quadriceps tendon into patella; into tibial tuberosity by patellar tendon
|
femoral nerve
|
extension of leg
|
|
quadriceps femoris, vastus medialis
|
upper end and shaft of femur
|
quadriceps tendon into patella; into tibial tuberosity by patellar tendon
|
femoral nerve
|
extension of leg
|
|
quadriceps femoris, vastus intermedius
|
shaft of femur
|
quadriceps tendon into patella; into tibial tuberosity by patellar tendon
|
femoral nerve
|
extension of leg
|
|
Muscles of Medial Compartment of Thigh
|
||||
|
gracilis
|
inferior ramus of pubis; ramus of ischium
|
upper part of shaft of tibia on medial surface
|
obturator nerve
|
adducts thigh and flexes leg
|
|
adductor longus
|
body of pubis
|
posterior surface of shaft of femur
|
obturator nerve
|
adducts thigh; assists in lateral rotation
|
|
adductor brevis
|
inferior ramus of pubis
|
posterior surface of shaft of femur
|
obturator nerve
|
adducts thigh; assists in lateral rotation
|
|
adductor magnus
|
inferior ramus of pubis; ramus of ischium, ischial tuberosity
|
posterior surface of shaft of femur near linea aspera; adductor tubercle of femur
|
obturator nerve; tibial nerve to hamstring part
|
adducts thigh and assists in lateral rotation; hamstring part extends thigh
|
|
Muscles of Posterior Compartment of Thigh
|
||||
|
biceps femoris
|
long head from ischial tuberosity; short head from shaft of femur
|
head of fibula
|
long head:tibial; short head:common peroneal
|
flexes and laterally rotates leg; long head extends thigh
|
|
semitendinosus
|
ischial tuberosity
|
upper part medial surface of shaft of tibia
|
tibial nerve
|
flexes and medially rotates leg; extends thigh
|
|
semimembranosus
|
ischial tuberosity
|
medial condyle of tibia; forms oblique popliteal ligament
|
tibial nerve
|
flexes and medially rotates leg; extends thigh
|
|
adductor magnus (hamstring part)
|
ischial tuberosity
|
adductor tubercle of femur
|
tibial nerve
|
extends thigh
|
|
Muscles of Anterior Compartment of the Leg
|
||||
|
tibialis anterior
|
shaft of tibia and interosseous membrane
|
medial cuneiform & base of first metatarsal
|
deep peroneal nerve
|
extends the foot; inverts foot at subtalar and transverse tarsal joints; supports medial longitudinal arch
|
|
extensor digitorum
|
shaft of fibula and interosseous membrane
|
extensor expansion of lateral four toes
|
deep peroneal nerve
|
extends toes; dorsiflexes (extends) foot
|
|
peroneus tertius
|
shaft of fibula & interosseous membrane
|
base of 5th metatarsal bone
|
deep peroneal nerve
|
dorsiflexes (extends) foot; everts foot at subtalar and transverse tarsal joints
|
|
extensor hallucis longus
|
shaft of fibula & interosseous membrane
|
base of distal phalanx of big toe
|
deep peroneal nerve
|
extends big toe; dorsiflexes (extends) foot; inverts foot at subtalar and transverse tarsal joints
|
|
Muscles of Lateral Compartment of Leg
|
||||
|
peroneus longus
|
shaft of fibula
|
base of 1st metatarsal & medial cuneiform
|
superficial peroneal nerve
|
plantar flexes foot; everts foot at subtalar & transverse tarsal joints; supports lateral longitudinal and transverse arches of foot
|
|
peroneus brevis
|
shaft of fibula
|
base of 5th metatarsal bone
|
superficial peroneal nerve
|
plantar flexes foot; everts foot at subtalar & transverse tarsal joints; supports lateral longitudinal arch
|
|
Muscles of Posterior Compartment of the Leg
|
||||
|
gastrocnemius
|
medial and lateral condyles of femur
|
by way of Achilles tendon to calcaneum
|
tibial nerve
|
plantar flexes foot; flexes leg
|
|
plantaris
|
lateral supracondylar ridge of femur
|
calcaneum
|
tibial nerve
|
plantar flexes foot; flexes leg
|
|
soleus
|
shafts of tibia and fibula
|
by way of achilles tendon into calcaneum
|
tibial nerve
|
with gastrocnemius & plantaris is powerful plantar flexor of foot; provides main propulsive force in walking & running
|
|
popliteus
|
lateral condyle of femur
|
shaft of tibia
|
tibial nerve
|
flexes leg; unlocks full extension of knee by laterally rotating femur on tibia
|
|
flexor digitorum longus
|
shaft of tibia
|
distal phalanges of lateral four toes
|
tibial nerve
|
flexes distal phalanges of lateral four toes; plantar flexes foot; supports medial and lateral longitudinal arches of foot
|
|
flexor hallucis longus
|
shaft of fibula
|
base of distal phalanx of big toe
|
tibial nerve
|
flexes distal phalanx of big toe; plantar flexes foot; supports medial longitudinal arch
|
|
tibialis posterior
|
shafts of tibia and fibula & interosseous membrane
|
tuberosity of navicular bone
|
tibial nerve
|
plantar flexes foot; inverts foot at subtalar and transverse tarsal joints; supports medial longitudinal arch of foot
|
|
Muscles on the Dorsum of Foot
|
||||
|
extensor digitorum brevis
|
Calcaneum
|
by four tendons into the proximal phalanx of big toe and long extensor tendons to 2nd, 3rd and 4th toes
|
deep peroneal nerve
|
extends toes
|
|
Muscles of the Sole of the Foot (First Layer)
|
||||
|
abductor hallucis
|
medial tubercle of calcaneum; flexor retinaculum
|
medial side, base of proximal phalanx of big toe
|
medial plantar nerve
|
flexes, abducts big toe; supports medial arch
|
|
flexor digitorum brevis
|
medial tubercle of calcaneum
|
middle phalanx of four lateral toes
|
medial plantar nerve
|
flexes lateral four toes; supports medial & lateral longitudinal arches
|
|
abductor digiti minimi
|
medial & lateral tubercles of calcaneum
|
lateral side base of proximal phalanx 5th toe
|
lateral plantar nerve
|
flexes, abducts 5th toe; supports lateral longitudinal arch
|
|
muscles of Sole of Foot (Second Layer)
|
||||
|
flexor accessorius (quadratus plantae)
|
medial and lateral sides of calcaneum
|
tendons flexor digitorum longus
|
lateral plantar nerve
|
aids long flexor tendon to flex lateral four toes
|
|
flexor digitorum longus tendon
|
shaft of tibia
|
base of distal phalanx of lateral four toes
|
tibial nerve
|
flexes distal phalanges of lateral four toes; plantar flexes foot; supports longitudinal arch
|
|
lumbricals
|
tendons of flexor digitorum longus
|
dorsal extensor expansion of lateral four toes
|
1st lumbrical from medial plantar; remainder lumbricals from deep branch of lateral plantar nerve
|
extends toes at interphalangeal joints
|
|
flexor hallucis longus
|
shaft of fibula
|
base of distal phalanx of big toe
|
tibial nerve
|
flexes distal phalanx of big toe; plantar flexes foot; supports medial longitudinal arch
|
|
Muscles of Sole of Foot (Third Layer)
|
||||
|
flexor hallucis brevis
|
cuboid, lateral cuneiform bones; tibialis posterior insertion
|
medial & lateral sides of base of proximal phalanx of big toe
|
medial plantar nerve
|
flexes metatarsophalangeal joint of big toe; supports medial longitudinal arch
|
|
adductor hallucis (oblique head)
|
bases of 2nd, 3rd & 4th metatarsal bones
|
lateral side base of proximal phalanx big toe
|
deep branch of lateral plantar
|
flexes big toe, supports transverse arch
|
|
adductor hallucis (transverse head)
|
plantar ligaments
|
lateral side of base of proximal phalanx big toe
|
deep branch of lateral plantar nerve
|
flexes big toe; supports transverse arch
|
|
flexor digiti minimi brevis
|
base of 5th metatarsal bone
|
lateral side of base of proximal phalanx of big toe
|
superior branch of lateral plantar nerve
|
flexes little toe
|
|
Muscles of Sole of Foot (Fourth Layer)
|
||||
|
dorsal interossei (4)
|
adjacent sides of metatarsal bones
|
bases of phalanges and dorsal expansion of corresponding toes
|
lateral plantar nerve
|
abduct toes with 2nd toe as the reference; flex metatarsophalangeal joints; extend interphalangeal joint
|
|
plantar interossei (3)
|
3rd, 4th, and 5th metatarsal bones
|
bases of phalanges & dorsal expansion of corresponding toes
|
lateral plantar nerve
|
adduct toes with 2nd toe as reference; flex metatarsophalangeal joints; extend interphalangeal joints
|
|
tendon of peroneus longus
|
see above
|
see above
|
see above
|
see above
|
|
tendon of tibialis posterior
|
see above
|
see above
|
see above
|
see above
|
The Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine 2010
Robert G. Edwards
Born: 27 September 1925, Batley, United Kingdom
Affiliation at the time of the award: University of Cambridge, Cambridge, United Kingdom
Prize motivation: “for the development of in vitro fertilization”
Robert is also known as “the father of the test tube baby”
Louise Brown, a health baby was born on July 25th, 1978 – the world’s first test tube baby. Since 1978, about 4 million babies have been born via IVF, some of whom are parents themselves
source: Nobel prize website
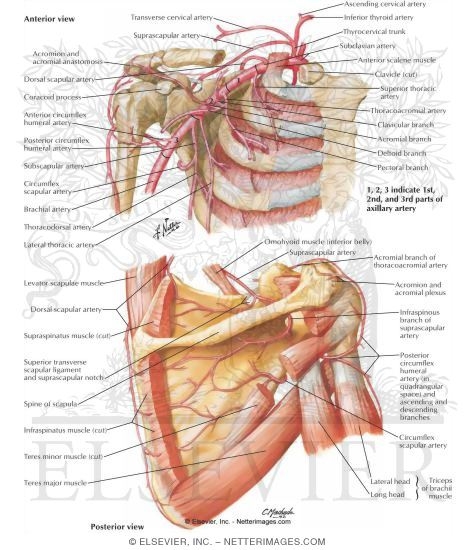
1. Pectoralis Major
origin- sternum, clavical and upper six costal cartilages
insertion- lateral lip of bicipital groove of humerus
nerve supply- lateral and medial pectoral nerves from brachial plexus.
2. pectoralis minor
origin- 3rd, 4th, 5th ribs
insertion- coracoid process of scapula
3. Subscapularis
origin- 1st costal cartilage
insertion- clavicle
nerve supply- nerve to subscapularis from the upper trunk of brachial plexus.
4. Serratus anterior
Origin- upper 8 ribs
Insertion- medial border and inferior bordrer if scapula
Nerve supply- long thoracic nerve
Muscles connecting upper limb tovertebral column
1. Trapezius-
Origin- Occipital bone, ligamentum nuchae, spine of 7th cervical vertebrae, spines of all thoracic vertebrae
Insertion- upper fibers in to lateral 3rd of clavicle, middle & lower fibers into acromion and spine of scapula
Nerve supply- spinal part of accessory nerve and C3 and C4
2. Latissumus dorsi
Origin- iliac crest, lumber fascia, spines of lower thoracic vertebrae, lower 3 or 4 ribs, and inferior angle of scapula
Insertion- floor of bicipital groove of humerus
Nerve supply- thoraco dorsal nerve
3. Lavator scapulae
Origin- transverse processes of 1st four cervical vertebrae
Insertion- medial border of scapula
Nerve supply- 3 and 4 and dorsal scapular nerve
Rhomboid minor
Origin- ligamentum nuchae, and spines of 7thcervical anf first thoracic vertebrae
Insertion- medial border of scapula
Nerve supply- dorsal scapular nerve
What is blood??
2) Blood connects the body systems together bringing the needed oxygen, nutrients, hormones and other signaling molecules, and removing the wastes.